
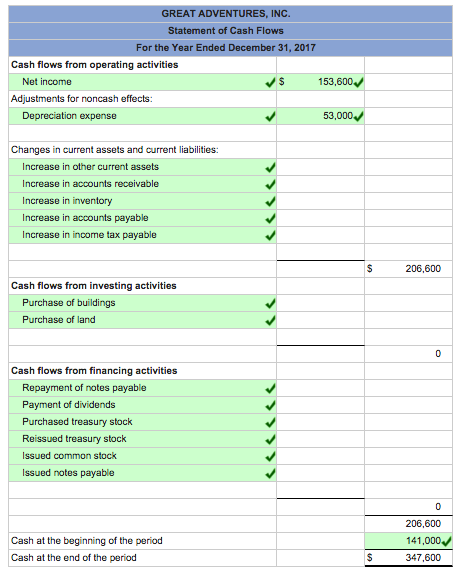
Question: The final financial statement is the statement of cash flows. Because no assets are held by a company without a source, the equation (and, hence, the balance sheet) must balance.Īssets = the total source of those assets The right side provides information to show how those assets were derived (from liabilities, from investors, or from operations). One way to understand the accounting equation is that the left side (the assets) presents a picture of the future economic benefits that the reporting company holds. There are no other ways to increase assets. If a business or other organization has an increase in its total assets, that change can only be caused by (a) an increase in liabilities such as money being borrowed, (b) an increase in capital stock such as additional money being contributed by stockholders, or (c) an increase created by operations such as a sale that generates a rise in net income. This equation stays in balance for one simple reason: assets must have a source. Or if the stockholders’ equity account is broken down into its component parts,Īssets = liabilities + capital stock + retained earnings. This is known as the accounting equation:Īssets = liabilities + stockholders’ equity. What creates that equilibrium?Īnswer: The balance sheet will always balance unless a mistake is made.
#Statement of cash flows sample problems plus
Thus, assets equal liabilities plus stockholders’ equity. The asset total of $1,206,000 is exactly the same as the liabilities ($577,000) plus the two stockholders’ equity accounts ($629,000-the total of capital stock and retained earnings). Why does the balance sheet balance? This agreement cannot be an accident. For convenience, a general term such as “stockholders’ equity” or “shareholders’ equity” encompasses the capital stock and the retained earnings balances. The retained earnings balance of $450,000 was computed earlier in Figure 3.4 “Statement of Retained Earnings” and identifies the portion of the net assets generated by the company’s own operations over the years. The $179,000 capital stock figure indicates the amount of assets that the original owners contributed to the business. Liabilities for salaries, insurance, and the like reflect debts that are owed at the end of year. Assets such as cash, inventory, and land provide future economic benefits for a company. Question: Considerable information is included on the balance sheet presented in Figure 3.5 “Balance Sheet”. Link to multiple-choice question for practice purposes: The balance sheet discloses assets and liabilities as of the one specified date. All the other financial statements report events occurring over a period of time (often a year or a quarter). The balance sheet shows the company’s financial condition on one specific date. The current assets can also be divided by current liabilities ($161,000/$57,000) to determine the company’s current ratio (2.82 to 1.00), another figure calculated by many decision makers as a useful measure of short-term operating strength. This labeling aids financial analysis because Davidson Groceries’ current liabilities ($57,000) can be subtracted from its current assets ($161,000) to arrive at a figure often studied by interested parties known as working capital ($104,000 in this example). Likewise, liabilities are split between current (to be paid during the next year) and noncurrent (not to be paid until after the next year). Note that the assets are divided between current (those expected to be used or consumed within the next year) and noncurrent (those expected to remain within the company for longer than a year). A picture is provided of each future economic benefit owned or controlled by the company (its assets) as well as its debts (liabilities).Ī typical balance sheet is reported in Figure 3.5 “Balance Sheet” for Davidson Groceries. All assets are listed first-usually in order of liquidity 1-followed by the liabilities. If a decision maker studies a company’s balance sheet (on its Web site, for example), what information can be discovered?Īnswer: The primary purpose of a balance sheet is to report an organization’s assets and liabilities at a particular point in time. Question: The third financial statement is the balance sheet. Identify the three sections of a statement of cash flows and explain the types of events included in each.Provide the reason for a balance sheet to always balance.Calculate working capital and the current ratio.
Explain the difference between current assets and liabilities and noncurrent assets and liabilities.List the types of accounts presented on a balance sheet.At the end of this section, students should be able to meet the following objectives:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
